9 Best Practices for API Security ⚔️
#87: Break Into API Security (7 Minutes)
Get my system design playbook for FREE on newsletter signup:
This post outlines API security best practices. You will find references at the bottom of this page if you want to go deeper.
Share this post & I'll send you some rewards for the referrals.
I created the block diagrams in this newsletter with Eraser.
Once upon a time, there was a two-person startup.
Yet they had only a few customers and limited features.
So they ran their site using a tiny number of application programming interfaces (APIs).
But one day, their site became extremely popular.
So they set up a microservices architecture for scalability.
Yet they knew little about API security.
And sent sensitive data in plain text through the API.
Also some of their public APIs often failed because of spiky traffic.
Besides it became difficult to keep APIs secure as they added more features.
So they researched the best practices to secure APIs.
Onward.
CodeRabbit: Free AI Code Reviews in VS Code - Sponsor
CodeRabbit brings real-time, AI-powered code reviews straight into VS Code, Cursor, and Windsurf. It lets you:
Get contextual feedback on every commit, not just at the PR stage
Catch bugs, security flaws, and performance issues as you code
Apply AI-driven suggestions instantly to implement code changes
Do code reviews in your IDE for free and in your PR for a paid subscription
API Security Best Practices
Here’s what they learned:
1. HTTPS
HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
Think of HTTP as a set of rules for transferring information on the Internet.
But it sends data in plaintext without encryption. It means someone on the public network can easily access or change the information. Thus making it insecure.
So it’s necessary to have Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) on the API.
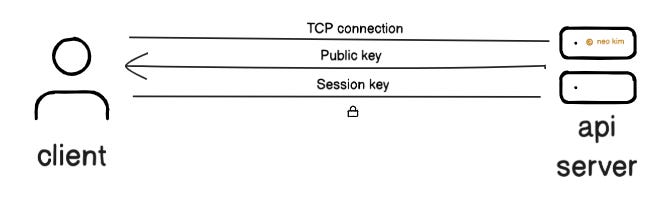
HTTPS encrypts data before sending it. Imagine HTTPS as HTTP running over an extra protocol to keep information secure.
The extra protocol is called Transport Layer Security (TLS). Think of TLS as a technique to encrypt data sent between the client and server.
Here's how it works:
The client connects to the API endpoint
The server gives a digital certificate to prove its identity
The browser checks the certificate against the trusted certificate authorities
Both sides agree on a shared encryption key
Then each request gets encrypted with that key
Thus making it secure.
Here are some best practices:
Use the latest version of TLS supported by the platform
Use HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)
Use strong ciphers
HSTS gets sent as an HTTP response header (Strict-Transport-Security). It tells the browser always to use HTTPS for this domain for a specific period.
While strong ciphers, such as AES or ChaCha20, ensure the encrypted connection is secure.
Let’s keep going!
2. Authentication
Anybody on the internet can call a public API.
Yet only verified users should access the data. So API authentication is necessary; it verifies a user’s identity before giving them system access.
Here are some best practices:
Use OAuth and OpenID Connect (OIDC)
Think of OAuth as a standard protocol for authorization
The client asks for access to the system
The authorization server checks the identity and gives them a token
The API then checks the token before allowing any action
While OIDC is a standard way to handle user authentication on top of OAuth
Use multi-factor authentication (MFA)
It adds extra steps to the authentication for security
The client logs in with their username and password
The system asks for an MFA code from the authenticator app
The authorization server gives a token only if both checks pass
The API then checks the token before allowing any action
Use short-lived tokens
Keep the token lifespan short
And refresh them often to reduce risk if a token gets stolen
Ready for the next technique?
3. Authorization
Authorization decides what an authenticated client may do in a system.
Imagine authentication as permission to enter a building. While authorization is like the key to enter only specific rooms once inside.
Here are some best practices:
Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Group users by their responsibility or function
Give separate permissions to each role
Then assign users to specific roles so they get access permissions
The system checks the role permissions before allowing actions
Use clear permission policies
Write clear rules that explain who can access what and when
Review and update permissions regularly to match the latest responsibilities
Proper access control reduces risk. So always give only the least privilege needed to get the job done.
Ready for the best part?
4. Rate Limiting and Throttling
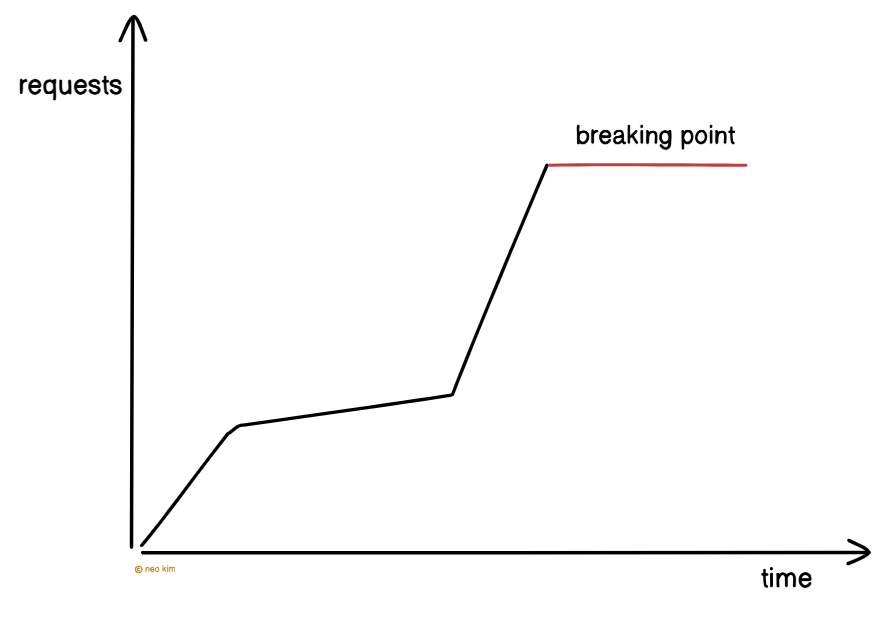
A popular API might get too many requests at once.
And this can overload the server and affect its performance. So it’s necessary to rate limit and throttle requests.
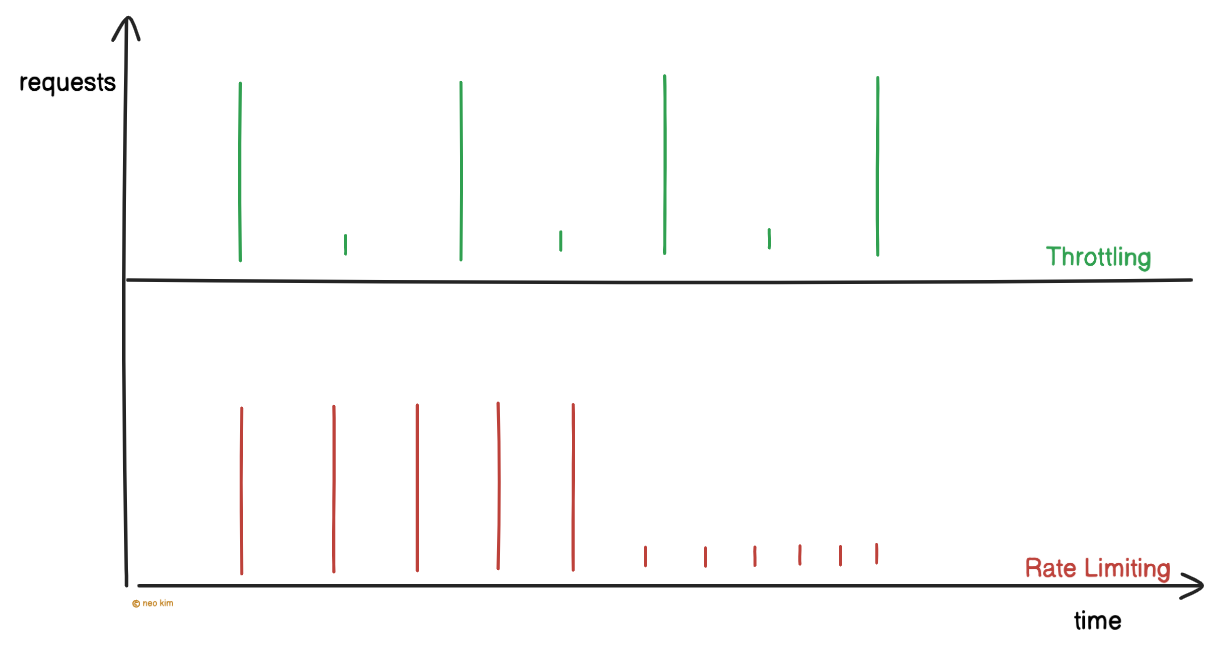
Rate limiting means controlling the number of requests a client can make to an API within a time window. It protects the API from abuse.
Here’s how it works:
The client sends requests through a rate limiter
The rate limiter tracks requests from a client by its IP address, user ID, or API key
The extra requests get rejected if the limit exceeds (response status code:
429 Too Many Requests)The counter then resets after the time window ends
Throttling means slowing down requests instead of dropping them. It adds a delay between requests using a queue. Thus preventing server overload.
Rate limits and throttling keep an API stable. Yet it has to be configured properly for a good user experience.
5. Input Validation
There’s a risk of some requests being malformed or malicious. So it’s necessary to validate and sanitize requests before processing them.
Validation checks the request structure, while sanitization removes unsafe data.
Here’s how it works:
Use schema validation to ensure the request has the expected structure
Sanitize requests using proven libraries and tools to block malicious content
This prevents malicious scripts, SQL injections, and malformed data.
SQL injection means sending malicious commands to the database via API requests. Think of it like smuggling prohibited items inside a shampoo bottle at airport security.
Only safe requests should reach the system. So validate and sanitize public APIs.
6. Logging and Monitoring
Prevention is better than cure.
Because of this, it’s necessary to track API activity for unusual traffic or suspicious behavior. Think of it like having security cameras and alarms for safety.
Here are some best practices:
Log metadata, such as IP address, timestamp, and headers; but avoid sensitive data
Use dashboards or security information and event management (SIEM) tools to find anomalies and raise alerts
SIEM collects logs from different services and analyzes them to find suspicious activity.
Monitoring turns logs into early warnings. So use them to avoid API abuse before it causes damage.
Let’s keep going!
Subscribe to get simplified case studies delivered straight to your inbox:
7. Security Audit
There is a risk of misconfiguration and security vulnerabilities. So it’s necessary to perform security audits regularly.
A security audit means checking the system to find and fix vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. Think of it like hiring a locksmith to test all the doors in the house to ensure they lock properly.
Here are some best practices:
Fuzz test APIs with unexpected inputs to catch bugs or failures
Stress test APIs by overloading them with many calls to check if they stay reliable
Security audits expose vulnerabilities. So use them to fix issues early.
8. Dependency Management
Third-party code may contain hidden vulnerabilities.
And a system is only as secure as its weakest part. So it’s necessary to keep libraries and frameworks up to date.
Imagine APIs as a city’s traffic control system. If a traffic light fails, accidents might happen.
Here are some best practices:
Track vulnerable dependencies using tools like Dependabot, Snyk, or npm audit
Patch security problems early
Remove unused dependencies
Ready for the best technique?